Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing industries worldwide, with healthcare experiencing some of the most transformative changes. From early disease detection to optimizing hospital workflows, AI is driving unprecedented levels of precision, efficiency, and personalized care.
In 2025, the global AI in healthcare market is valued at $21.66 billion, a significant increase from $14.92 billion in 2024, reflecting a robust compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 38.6% from 2025 to 2030, with a projected valuation of $110.61 billion by 2030 [Source: MarketsandMarkets]. As AI adoption accelerates, understanding its transformative role in modern healthcare is critical for stakeholders and patients alike.
What Is Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare?
Artificial intelligence in healthcare involves advanced algorithms and software that mimic human cognitive processes to analyze and interpret complex medical data. Unlike traditional systems, AI learns and adapts over time, enhancing its performance with experience.
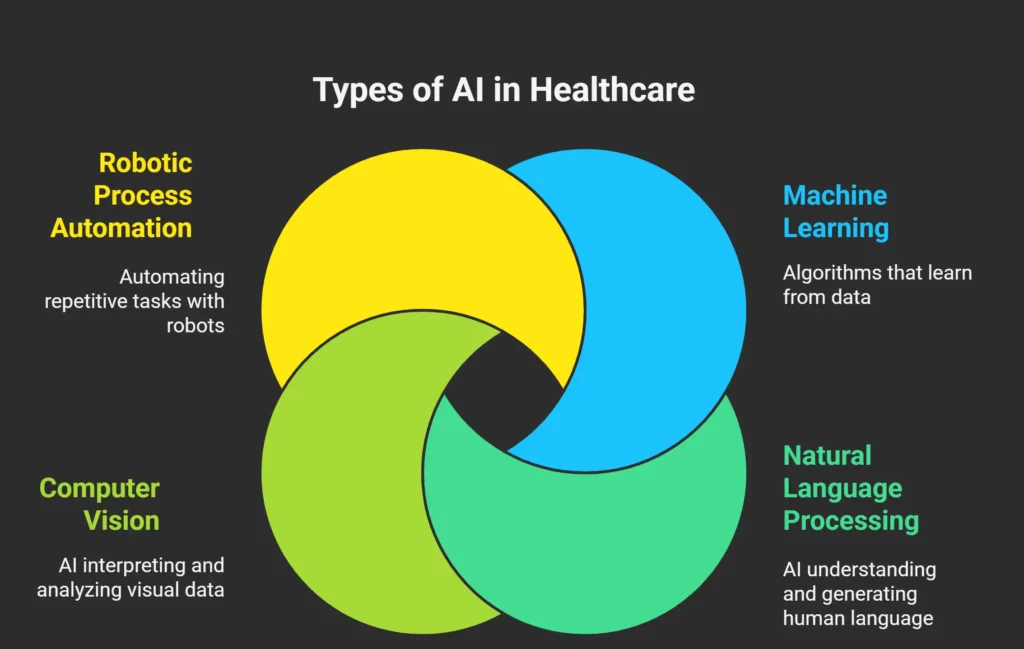
Types of AI in Healthcare:
- Machine Learning (ML): Enables predictive analytics, risk assessment, and pattern recognition.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Powers medical transcription, clinical documentation, and voice-activated assistants.
- Computer Vision: Analyzes medical images such as MRIs, CT scans, and X-rays.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Streamlines repetitive administrative tasks.
Also find: The Role of AI in Hospital Management Systems
Key Applications of AI in Modern Healthcare
1. Medical Imaging and Diagnostics
AI algorithms are transforming medical imaging by detecting conditions with remarkable accuracy. For instance, Google Health’s AI model for breast cancer detection achieved 11.5% fewer false positives and 5.7% fewer false negatives compared to human radiologists.
2. Drug Discovery and Development
AI accelerates drug discovery by analyzing vast molecular datasets. Atomwise, for example, uses deep learning to screen billions of compounds in hours, potentially reducing drug development costs by $2.6 billion and timelines by up to 10 years per candidate.
3. Personalized Medicine
AI tailors treatments to individual patients using genetic and clinical data. IBM Watson Health leverages genomic sequencing to personalize cancer therapies, improving treatment outcomes.
4. Virtual Health Assistants and Chatbots
AI-powered tools like Babylon Health and Ada Health provide 24/7 symptom assessments, health advice, and appointment scheduling, reducing unnecessary hospital visits by up to 45%.
5. Predictive Analytics for Patient Monitoring
AI-driven wearables monitor vital signs and predict adverse events. Current Health’s AI platform has reduced ICU admissions by 19% by forecasting patient deterioration.
6. Robotic Surgery
AI-enhanced systems like the da Vinci Surgical System improve surgical precision, resulting in 21% fewer complications and faster recovery times.
7. Administrative Automation
AI optimizes hospital operations by automating billing, claims processing, and data management. By 2026, AI is projected to save the U.S. healthcare system $150 billion annually in administrative costs [Source: Accenture, “AI in Healthcare Savings,” 2024].
Benefits of AI in Healthcare
- Early and Accurate Diagnosis: AI detects diseases like cancer, Alzheimer’s, and diabetic retinopathy with high precision, often identifying conditions before symptoms manifest, leading to better outcomes.
- Operational Efficiency: Automates administrative tasks, reducing hospital wait times and staff burnout. For example, AI-driven scheduling systems improve patient flow by 30% in high-volume facilities.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Enhances treatment efficacy by tailoring therapies to individual genetic profiles, lifestyles, and medical histories, increasing patient satisfaction rates by 25%.
- Cost Reduction: Minimizes diagnostic errors and redundant testing, saving an estimated $200 billion annually globally by avoiding unnecessary procedures.
- Remote Care Access: Expands healthcare availability for rural and underserved populations through telemedicine and AI-powered diagnostics, increasing access by 40% in remote regions.
- Improved Patient Engagement: AI chatbots and virtual assistants empower patients to manage their health proactively, with 60% of users reporting better adherence to treatment plans.
- Enhanced Research Capabilities: AI accelerates medical research by analyzing vast datasets, enabling breakthroughs in areas like genomics and epidemiology, reducing research timelines by up to 50%.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its promise, AI in healthcare faces significant challenges:
- Data Privacy and Security: In 2024, U.S. healthcare data breaches of 500 or more records resulted in the exposure or theft of 276,775,457 health records, a significant increase from the 168 million records compromised in 2023. This figure includes the largest-ever healthcare data breach at Change Healthcare, affecting an estimated 190 million individuals due to a ransomware attack. The HIPAA Journal reports that 734 large healthcare data breaches were recorded in 2024, with an average of 758,288 records breached per day. Hacking/IT incidents, particularly ransomware attacks, were the leading cause, accounting for a significant portion of these breaches. This underscores the growing vulnerabilities in healthcare systems, particularly as AI and digital technologies increase the attack surface for sensitive data [Source: HIPAA Journal, “Healthcare Data Breach Statistics,” updated May 31, 2025].
- Algorithmic Bias: Non-diverse training data can lead to inaccurate outcomes for underrepresented groups, with studies showing up to 15% lower accuracy for minority populations in some AI models.
- Lack of Explainability: “Black box” AI models challenge clinician trust, with 70% of healthcare providers expressing concerns over uninterpretable AI decisions.
- Ethical Concerns: Accountability for AI-driven misdiagnoses remains unresolved, raising questions about liability in cases of adverse outcomes.
- Integration Barriers: Legacy hospital systems often lack compatibility with modern AI tools, with 50% of hospitals reporting integration challenges.
- Regulatory Gaps: Evolving AI technologies outpace current regulations, creating uncertainty around approval and deployment standards.
- High Implementation Costs: Initial costs for AI adoption, including infrastructure and training, can exceed $1 million for mid-sized hospitals, limiting adoption in resource-constrained settings.
Future Trends in AI and Healthcare
- Generative AI: Tools like DeepMind’s AlphaFold are revolutionizing protein structure prediction, accelerating drug discovery and personalized medicine.
- AI and IoT Integration: Wearables paired with AI will provide real-time health insights, with 75% of patients expected to use AI-enabled wearables by 2027.
- Digital Twins: Virtual patient models enable precise treatment simulations, with early trials showing 30% improved treatment outcomes in oncology.
- Multimodal AI: Combines text, image, and audio data for holistic diagnostics, improving diagnostic accuracy by 20% in complex cases.
- AI-Driven Population Health Management: AI analyzes population health data to predict disease outbreaks and optimize resource allocation, reducing public health response times by 40%.
- Autonomous Healthcare Systems: AI-powered autonomous clinics, integrating robotics and diagnostics, are projected to serve 10% of outpatient visits by 2030.
- Ethical AI Frameworks: Advances in explainable AI and ethical guidelines will enhance trust, with 80% of healthcare organizations adopting ethical AI standards by 2027.
Learn here: Using Artificial Intelligence To Help Keep Your Financial Data Safe
Real-World Case Studies
- Mayo Clinic: AI detects heart arrhythmias with over 80% accuracy, improving early intervention.
- NHS England AI Lab: AI models for chest X-rays reduced reporting delays by 40%.
- Stanford University: Developed an AI system for skin cancer diagnosis that matches dermatologist performance.
Regulatory Landscape and Ethical Considerations
- U.S. HIPAA and EU GDPR enforce strict data privacy standards, requiring secure handling of patient data in AI applications to protect confidentiality and prevent unauthorized access.
- FDA’s AI/ML-based SaMD Action Plan (2023) provides a framework for ensuring safety, efficacy, and transparency of AI-driven medical devices, emphasizing pre-market evaluation and post-market monitoring.
- WHO’s 2024 Ethics Guidelines advocate for human oversight, equitable access, and transparency in AI healthcare applications to address disparities and ensure fair outcomes.
- Ethical AI Deployment: Healthcare providers must prioritize patient consent, transparency, and accountability, particularly in high-stakes scenarios like surgical interventions or terminal illness diagnoses, to maintain trust and ethical integrity.
- Global Harmonization Efforts: Initiatives like the International Medical Device Regulators Forum (IMDRF) are working to standardize AI regulations across countries, reducing compliance complexities.
- Bias Mitigation Standards: Regulatory bodies are increasingly mandating bias audits for AI algorithms to ensure equitable performance across diverse populations, with the EU proposing mandatory audits by 2026.
Ethical AI deployment requires transparency, patient consent, and accountability, especially in high-stakes scenarios like surgeries or terminal diagnoses.
Conclusion
In 2025, AI is a cornerstone of modern healthcare, driving advancements in diagnostics, treatment, and efficiency. While challenges like data security and bias persist, responsible implementation—guided by robust regulations and ethical frameworks—will ensure AI’s benefits are maximized. The future of healthcare lies in a collaborative synergy between human expertise and AI innovation.
Do you know: Smart Homes Using AI in India Opening Up New Possibilities
FAQs
AI supports diagnostics, treatment planning, robotic surgery, drug discovery, and administrative tasks.
It enhances diagnostic accuracy, reduces costs, improves patient outcomes, and expands remote care access.
No, AI augments doctors’ capabilities but cannot replicate human judgment or empathy.
Risks include data breaches, algorithmic bias, lack of transparency, and liability for errors.
Leaders include Google Health, IBM Watson Health, Microsoft Healthcare, DeepMind, NVIDIA, PathAI, and Tempus.
AI systems rely heavily on large datasets, including sensitive patient information. When properly implemented, AI systems follow strict protocols like HIPAA and GDPR to protect data privacy. However, risks remain, especially with cybersecurity vulnerabilities, making robust data encryption and ethical AI design crucial.
Professionals entering this space need a mix of healthcare domain knowledge and technical skills like data analytics, machine learning, and knowledge of medical regulations. Roles range from clinical data scientists to AI product managers and bioinformatics analysts.
AI integration often begins with pilot programs for diagnostics or automation in administrative tasks. Hospitals collaborate with AI vendors to train staff, validate models on localized data, and ensure interoperability with Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems.
While initial implementation costs can be high, AI has long-term potential to reduce costs through efficiency and automation. Solutions like AI-powered mobile diagnostics and telemedicine tools are becoming more accessible even in resource-constrained settings, especially with support from global health organizations.